Referencing AI Tools

AI misconduct
Using AI (Artificial Intelligence) can be helpful for things like coming up with ideas or making plans for your projects.
However, it is not acceptable to use them to do all the work of writing your essay or assignment for you. You should also keep in mind that some of these AI tools use ideas from other people’s work without saying where the ideas came from, which is often seen as plagiarism.
This is highlighted in the college’s Plagiarism Policy, found on the Documents and Policies website.
Always remember to use AI tools wisely, reference them properly, and give credit where it’s due.
Declaration of AI sources in your work
 If your tutors have stated that you may use AI sources in your assessed work, then any use should be declared.
If your tutors have stated that you may use AI sources in your assessed work, then any use should be declared.
As a minimum, the declaration should explain what AI tools you have used to generate content in the process of working on your assessment.
Unless specified otherwise by the teacher, you should use Harvard Referencing style for your work.
Learn how to reference the use of AI tools by expanding the information below:
Declaration of AI tools used
You must declare the AI tool used and to what extent. This declaration should be located at the end of your reference list.
You can do it in the following way:
- ‘No AI produced content has been presented as my own work.’
- ‘I have used the following AI tools: [Name of AI tool and URL link] to generate content for research / ideas generation / plans / self-study in my process during this assessment.’
- ‘I declare that I have used [Name of AI tool and URL link] to create content that was included within my assessment in a modified / paraphrased form.
Prompts used
Along with your declaration of AI tools used, you must explain how the content was generated. If the content came from a private conversation or prompt that isn’t publicly available (for example, a chat with an AI like Copilot), include the exact prompts you used and the unedited response of the tool. You should also describe how you altered it. This information should go in the appendix of your work.
You can do it in the following way:
- The following prompts were inputted into [AI tool]: [list prompts].
- The unaltered generated content was: [paste unaltered content that was generated by AI tool].
- I used / changed the generated content in the following ways: [explain actions taken].
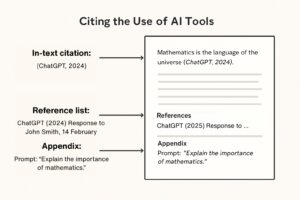
In-text citation
A Harvard in-text citation should appear in brackets every time you quote, paraphrase, or refer to an information from a source, including Generative AI tools. The in-text citation only points to the whole reference in the reference list at the end of your work.
The citation should appear directly after the text that uses a reference, and it has the following format:
(name of the AI tool, year the tool was used)
Referenced or paraphrased text
For example: Photosynthesis is essential because it enables plants to produce the energy they need to grow while releasing oxygen into the atmosphere (Copilot, 2025).
Direct quotation
If a text is directly quoted, it should be within quotation marks, for example: “Photosynthesis is how plants use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to make food and release oxygen” (Copilot, 2025).
Tool name included in text
If the name of the tool is included in the paragraph, simply write the year of the communication in the bracket after it, for example: Copilot (2025) suggested that without photosynthesis Earth wouldn’t exist as we know it.
Learn more about referencing AI tools by accessing the link.
Reference list
A reference list is the section at the end of your work that shows where you found your information and includes full details for each source. Your in-text citations always point to the reference list.
Publicly unavailable AI content
To reference AI tools in the Harvard style, where the information was only available to you in a private conversation with the AI, use the following order:
- Name of AI
- Year of communication (in round brackets)
- Medium of communication (how the information was received)
- Receiver of communication
- Day and month of communication
For example: OpenAI (2025) ChatGPT response to John Stephens, 14 August
Since the conversation with the AI was private, the full list of prompts, unedited AI responses, as well as the list of changes need to be included in the appendix (as described previously) for the person verifying the references.
Publicly available AI content
If you reference AI content that is publicly available, the order is slightly different:
Name of AI (Year) Title of work [Medium] Available at: DOI or URL (Accessed: date)
For example: Aperture Max (no date) A futuristic urban motorcycle [AI Image] Available at: https://lexica.art/prompt/7d48995f-f06b-496a-9c2b-3c00072cbf22 (Accessed: 14 August 2025)
If the content is publicly available, and you do not change it, you don’t have to list the prompt or declare the use of AI tools, as the content is treated as an existing art or writing with the AI as an author.
However, if you use AI tools to generate or modify content, you still need to declare it.
Learn more about referencing AI tools by accessing the link.
You can find more specific guidance on Harvard (and other) style referencing by accessing the link. If you’re unsure whether and how a part of your assignment should be cited, contact your teacher.
AI referencing example
Always check the extent of allowed AI use with your teacher.
The example features a fragment of a report on photosynthesis. For the assignment the use of AI-generated content was explicitly allowed by the teacher, with moderation. The student asked Microsoft Copilot for a creative analogy and included it as a direct quote. The student also used ChatGPT to highlight key stages of photosynthesis and paraphrased a part of the response into their work. Lastly, they have also included a publicly available AI-generated image.
Expand the tab below to see how this report should be referenced in the Harvard style. If you have any questions about the referencing standard or whether and how different content should be referenced, contact your teacher.
Example Assignment
Example Assignment Section
Photosynthesis is how plants, algae, and some bacteria use sunlight to make glucose. It mainly happens in the leaves, inside chloroplasts, where chlorophyll absorbs light. They take in carbon dioxide from the air and water from the soil to produce glucose for energy, releasing oxygen as a by-product. “Think of it like a solar-powered factory in a plant’s leaves, where sunlight provides the power, water and carbon dioxide are the raw materials, and sugar is the finished product” (Copilot, 2025).
The process has two stages: light-dependent reactions, in the thylakoid membranes, use sunlight to split water, release oxygen, and make ATP and NADPH (OpenAI, 2025). Light-independent reactions (Calvin Cycle), in the stroma, use these molecules to turn carbon dioxide into glucose.
Rest of the report…
References
- Copilot (2025) Copilot response to John Smith, 14 August
- OpenAI (2025) ChatGPT response to John Smith, 14 August
- Stable Diffusion XL (no date) The main components of a plant cell [AI image] Available at: https://stablediffusionweb.com/image/20472079-plant-cell-components (Accessed: 14 August)
No AI produced content has been presented as my own work. I declare that I have used Microsoft Copilot (https://copilot.microsoft.com/) and OpenAI ChatGPT (https://chatgpt.com/) to create content that was included within my assessment in a modified / paraphrased form.
Appendix
I used Microsoft Copilot to generate an analogy for the process of photosynthesis.
The following prompt was inputted into Copilot: “Give me a creative analogy to explain photosynthesis to a beginner.”
The full response was: “Think of it like a solar-powered factory in a plant’s leaves, where sunlight provides the power, water and carbon dioxide are the raw materials, and sugar is the finished product.”
The response was quoted directly and referenced in the text.
I used ChatGPT to produce a plain-language summary of photosynthesis before rewriting in my own words.
The following prompt was inputted into ChatGPT: “Summarise the stages of photosynthesis in plain language.”
The full response was:
“Photosynthesis happens in two main stages.
- Light-dependent reactions
These take place in the thylakoid membranes inside the chloroplasts. Sunlight is absorbed by chlorophyll, and this energy is used to split water molecules. This releases oxygen into the air and produces two energy-carrying molecules called ATP and NADPH. - Light-independent reactions (Calvin Cycle)
These happen in the stroma of the chloroplast. The ATP and NADPH made in the first stage are used to power a set of chemical steps that take in carbon dioxide from the air and turn it into glucose — a type of sugar the plant uses for energy and growth.”
I have used and paraphrased only the light-dependent reaction fragment of the the response and clearly referenced it. I have not used the response for the light-independent reaction section of my work.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Will I get in trouble or a disciplinary for using AI?
If you follow the guidance provided using AI correctly within the college’s guidance and plagiarism policy you will not need to worry about getting into trouble.
However, if you choose to ignore this and use AI in your work by copying and pasting full assignments or parts of, you may face disciplinary action.
Can I use AI to help with my assignments?
Using AI as a starting point is good practice. Questioning it about the topic your assignment is on, to gauge further insight and help with where to start can be extremely useful; as starting assignments is often the hardest part.
You just need to make sure you don’t copy and paste the information the AI gives you into your assignment.
How does AI work?
If you are interested in how generative AI actually works google has produced a great video that explains it well:
You can also find out more information here on Googles Blog feature: Ask a Techspert
Or finally, you could ask AI to explain it itself by signing up to ChatGPT.